Welding
A variety of joining techniques
tailored to different materials
We are committed to developing fine processed products using various joining techniques at MITSUWA.
Here, we introduce some representative joining techniques.
Laser Welding
In our manufacturing process, particularly in the production of products like electrodes for discharge lamps, we employ laser welding technology. This method allows us to minimize damage during bonding for high melting point materials such as tungsten and molybdenum.
- Examples of Tungsten-Molybdenum Joints

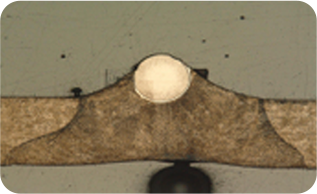
- Cross-section of tungsten-molybdenum joints

- Example of tungsten-SUS304 joints
Advantages
- Low distortion
- Concentrated heat minimizes
input into the base material
- Excellent finish
- Uniform beads with pulse control
- High joint flexibility
- Various joints possible
by adjusting the focal
point of the light
- Material versatility
- Can weld materials like aluminum,
stainless steel, brass, and titanium
(materials with high reflectivity are not suitable)
We also possess fiber lasers capable of welding high-reflectivity materials such as aluminum and stainless steel, as well as challenging-to-machine materials like brass and titanium. Please feel free to contact us for any welding inquiries you may have.
Resistance Welding
Resistance welding utilizes the heat generated by passing electric current through metals to join them. It is applied to various products by adjusting current, voltage, and pressure depending on the material.
- Examples of Resistance Welding

- Examples of Resistance Welding

- Examples of Resistance Welding

Brazing
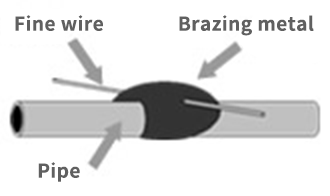
Brazing is a joining method using metal filler materials such as silver solder or nickel-based solder. It is commonly used for joining materials with vastly different thicknesses or for joining metal and non-metal materials. Due to our focus on fine materials, we perform brazing using lasers instead of gas torches.
Brazing Metal + Metal
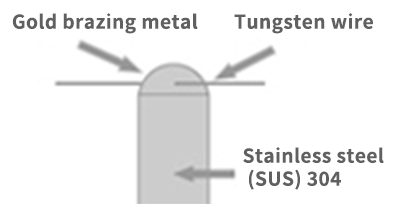
- Φ0.5mm SUS304 + Φ20μm W wire
- Joining 20μm wire to a Φ0.5mm SUS pin
Types and Characteristics of Lasers
- YAG Laser
- Components: Yttrium (Y), Aluminum (A), Garnet (G)
Wavelength: 1.064μm
Characteristics: High energy density, capable of pulse and continuous oscillation.
- CO2 Laser
- Components: Carbon dioxide gas
Wavelength: 10.6μm
Characteristics: High output power, not suitable for pinpoint precision but capable of continuous oscillation.
- Excimer Laser
- Components: Excimer (excited species)
Wavelength: Short wavelengths, typically 0.157μm (ultraviolet
laser) Characteristics: Short wavelength with relatively lower energy.
These lasers have different wavelengths and characteristics suitable for various industrial and application-specific needs.



